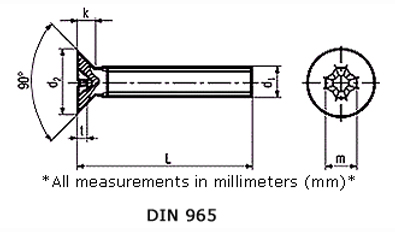
Brass Phillips Flat Countersunk Head Screws Din 965
The Philips flat head countersunk screw is designed in a specific way so that it can tap its own hole when it is driven into the material. For hard material surfaces such as metal or hard plastics, the self-tapping ability of the csk screw is often created by cutting a gap in the continuity of the thread on the countersunk screw, which creates a flute, and cutting edges similar to those on a tap.
Thus, when a regular machine screw is not able to tap its own hole in a metal surface, a self-tapping such screws can tap their holes. For softer surface materials such as wood or soft plastics, this self-tapping property can come simply from the tip that tapers to a certain point. Like the tip of a nail, such points form a hole by displacement of the surrounding material. Any chip-forming drilling/cutting/evacuating action can be prevented.
Brass Phillips Flat Countersunk Head Screws Din 965
4.8 Grade
Phillips Flat Head Countersunk
M060 -965-4.8 Zink Plated
DIN 965
ISO 7046
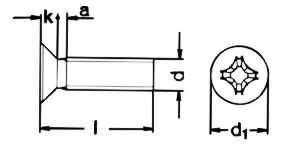
| Diameter | M2 | M2.5 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | - | 0.9 | 1 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 2 | 25 |
| k | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.65 | 2.2 | 25 | 3 | 4 |
| d1 | 3.8 | 4.7 | 5.6 | 7.5 | 9.2 | 11 | 14.5 |
| Driver Size | H1 | H1 | H1 | H2 | H2 | H3 | H4 |
| Length in (mm) | Pkg | ||||||
| 4 | 100 | ||||||
| 5 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||
| 6 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| 8 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 10 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| 12 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| 14 | 100 | ||||||
| 16 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 18 | 100 | ||||||
| 20 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 25 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 30 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| 35 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| 40 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| 45 | 100 | 100 | |||||
| 50 | 100 | 100 | |||||
| 60 | 100 | ||||||